|
PREPARING TO TEACH
Good
teaching facilitates students in constructing their own knowledge.
Planning learning objectives/outcomes in advance strives to map this process
out in advance.
|
TOPIC 2:
Course design: content & structure
|
Designed by Elena Berman |
| |
|
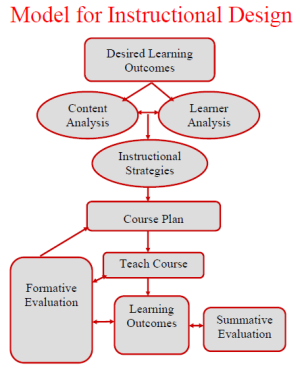
A
Model for Instructional Design
[pdf]
Content Analysis:
- decide on content & skills to
be acquired
-
determine desired learning outcomes
(i.e. how students will demonstrate
they have learned content, acquired skills)
-
write instructional objectives to achieve the
desired outcomes
Learner Analysis:
- assess
need for multiple learning styles
(know
your audience)
- determine cognitive
skills needed for
different levels
of "thinking
tasks"
Instructional Strategies:
-
develop learning activities using
"task
prompts"
that address content at
appropriate skill levels
- determine which modes of instruction
delivery
are
best suited to task
Put it all together into a Course Plan:
-define &
limit content (connect w/ texts)
- determine
logical arrangement for course content
-
construct course schedule (topics, assignments,
test dates or as much as
can be determined in
advance
-- build in flexibility)
Also:
Think about how you will communicate the course
plan and its logic to your students (concept map,
diagram, class explanation or discussion, etc.)
|
|
|
|
|
|
ASSIGNMENT
-
Read:
Lynch, C.L. Wolcott, S.K.(2001)
Helping Your Students Develop Critical Thinking
Skills [pdf]
Tools for
Teaching (2nd ed ): Chapter 1
Designing or Revising a Course
Decide on a
course (or course module) you intend to use as the
basis for this and subsequent assignments in this class.
-
Write a draft of a
one-paragraph description
of your course or module, (i.e., a
piece that might appear in the course description section of a syllabus or
at the beginning of a class learning activity.)
-
Make a list of the main content (topics) you
want to cover in your course or course learning module
-
Write
three to five (3-5)
instructional objectives for the
course or course module you've selected.
NOTE: for our purposes, the
terms "instructional objectives," "learning objectives," and
"learning outcomes" will be used interchangeablly, and mean
a statment of what learners will be able to do, or perform,
to be considered competent after the instruction takes
place.
Help on writing
objectives can be found under Useful Background Reading
below:
Be prepared to share
your assignment with the rest of the class on Wed Jan 26th.
___________________________________________________________________
USEFUL BACKGROUND READING TO ASSIST YOU IN
COMPLETING THE ASSIGNMENT:
Tools for Teaching (2nd ed ):
Chapter 1 Designing or Revising a Course
Course design and planning
- Read “Designing a Course” from
excellent
Course Design Site of The Teaching Center of Washington University of St.
Louis. https://teachingcenter.wustl.edu/resources/course-design/
- See also Washington University of St. Louis's (rather ambitious!)
"Planning a Course Timeline":
https://teachingcenter.wustl.edu/resources/course-design/course-planning-timeline/
Desired Outcomes
- Visit and
browse the UA University-Wide General Education Committee’s webpage on Expected Outcomes
for General Education courses:
http://gened.arizona.edu/faculty/expected-outcomes
Writing
Learning Objectives
- See the
following information on
Developing Course Objectives from the
Illinois Online Network
- See
“Writing Objectives Using Bloom's Taxonomy” from
UNC Charlotte's Center for
Teaching and Learning
(has very useful charts with keywords and sample
wording)
Learner
Analysis
Learning Styles
(Optional:
For those who want to learn more about various theories on how students learn.
For insights on your own learning style,complete the assessments under Topic 1b if you haven't done so already)
Review:
Felder, R.M.
Matters of Style [pdf]
also at:
http://www.ncsu.edu/felder-public/Papers/LS-Prism.htm
Explore:
more about learning styles from Richard Felder and
his collaborators, including the Index of Learning Styles
(ILS) and how the Myers-Briggs Indicator types relate to
teaching and learning:
More on cognitive
skills & learning styles
|